程序过滤
校准机器人后,可通过以下两种方式应用校准参数::
●过滤现有程序:自动修正程序中所有目标点坐标以提升运动精度,支持手动操作或API调用
●离线编程生成优化程序:通过RoboDK生成的程序已内置校准参数(含API生成程序)。
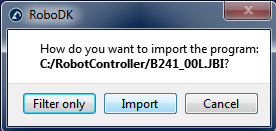
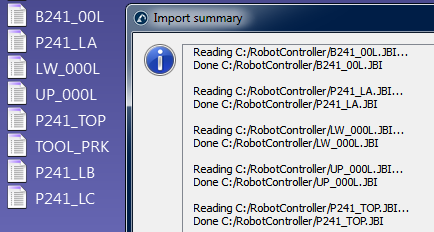
要手动过滤现有程序:将机器人程序文件拖放到RoboDK的主屏幕上(或选择文件➔打开),然后选择仅过滤。程序将被过滤并保存在同一文件夹中。过滤摘要将提及过滤算法是否存在问题。如果你想在RoboDK中模拟程序,也可以选择导入程序。如果程序有任何依赖关系(工具坐标系或基本坐标系定义、子程序......),它们必须位于导入第一个程序的同一目录中。
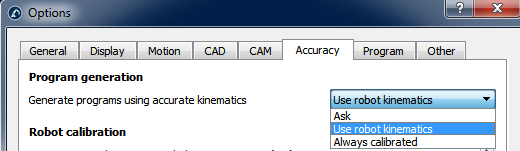
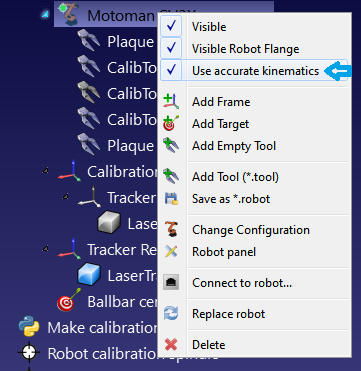
将程序导入RoboDK后,你可以在有或没有绝对精度的情况下重新生成程序。在RoboDK的主要精度设置中(工具➔选项➔精度),你可以决定是否始终使用精确运动学生成程序,是否希望RoboDK每次都询问,或者是否希望使用当前的机器人运动学。右击机器人,激活/禁用标签:使用机器人运动学模型,即可更改当前机器人运动学。如果激活,则会看到一个绿点;如果未激活,则会看到一个红点。
使用API过滤程序
在给机器人和机器人程序校准过的情况下,使用RoboDK可以通过调用FilterProgram过滤整个程序:
robot.FilterProgram(file_program)
在资源库的"宏"部分,有一个名为"过滤程序"(FilterProgram)的宏示例。以下代码是使用RoboDKAPI过滤程序的Python脚本示例。
from robolink import * # API to communicate with RoboDK
from robodk import * # basic matrix operations
import os # Path operations
# Get the current working directory
CWD = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
# Start RoboDK if it is not running and link to the API
RDK = Robolink()
# optional: provide the following arguments to run behind the scenes
#RDK = Robolink(args='/NOSPLASH /NOSHOW /HIDDEN')
# Get the calibrated station (.rdk file) or robot file (.robot):
# Tip: after calibration, right click a robot and select "Save as .robot"
calibration_file = CWD + '/KUKA-KR6.rdk'
# Get the program file:
file_program = CWD + '/Prog1.src'
# Load the RDK file or the robot file:
calib_item = RDK.AddFile(calibration_file)
if not calib_item.Valid():
raise Exception("Something went wrong loading " + calibration_file)
# Retrieve the robot (no popup if there is only one robot):
robot = RDK.ItemUserPick('Select a robot to filter', ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT)
if not robot.Valid():
raise Exception("Robot not selected or not available")
# Activate accuracy
robot.setAccuracyActive(1)
# Filter program: this will automatically save a program copy
# with a renamed file depending on the robot brand
status, summary = robot.FilterProgram(file_program)
if status == 0:
print("Program filtering succeeded")
print(summary)
calib_item.Delete()
RDK.CloseRoboDK()
else:
print("Program filtering failed! Error code: %i" % status)
print(summary)
RDK.ShowRoboDK()
使用API过滤目标
以下代码是一个 Python 脚本示例,使用 FilterTarget 命令,利用 RoboDK API 过滤目标(位姿目标或关节目标):
pose_filt, joints = robot.FilterTarget(nominal_pose, estimated_joints)
如果第三方应用程序(RoboDK 除外)使用位姿目标生成机器人程序,本示例将非常有用。
Note:如果程序是使用 API 自动生成的,则不需要这样做。
from robolink import * # API to communicate with RoboDK
from robodk import * # basic matrix operations
def XYZWPR_2_Pose(xyzwpr):
return KUKA_2_Pose(xyzwpr) # Convert X,Y,Z,A,B,C to a pose
def Pose_2_XYZWPR(pose):
return Pose_2_KUKA(pose) # Convert a pose to X,Y,Z,A,B,C
# Start the RoboDK API and retrieve the robot:
RDK = Robolink()
robot = RDK.Item('', ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT)
if not robot.Valid():
raise Exception("Robot not available")
pose_tcp = XYZWPR_2_Pose([0, 0, 200, 0, 0, 0]) # Define the TCP
pose_ref = XYZWPR_2_Pose([400, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]) # Define the Ref Frame
# Update the robot TCP and reference frame
robot.setTool(pose_tcp)
robot.setFrame(pose_ref)
# Very important for SolveFK and SolveIK (Forward/Inverse kinematics)
robot.setAccuracyActive(False) # Accuracy can be ON or OFF
# Define a nominal target in the joint space:
joints = [0, 0, 90, 0, 90, 0]
# Calculate the nominal robot position for the joint target:
pose_rob = robot.SolveFK(joints) # robot flange wrt the robot base
# Calculate pose_target: the TCP with respect to the reference frame
pose_target = invH(pose_ref)*pose_rob*pose_tcp
print('Target not filtered:')
print(Pose_2_XYZWPR(pose_target))
joints_approx = joints # joints_approx must be within 20 deg
pose_target_filt, real_joints = robot.FilterTarget(pose_target, joints)
print('Target filtered:')
print(real_joints.tolist())
print(Pose_2_XYZWPR(pose_target_filt))