This example shows how to load a sample RoboDK station (default setup) and follow a set of curves defined in Rhino with the robot.
1.Load the Dome example in Rhino.
2.Select the RoboDK tab and select ![]() Settings.
Settings.
3.Select Load Project…
4.Select Default Setup. RoboDK will start and load a sample project with a KUKA robot, one tool (a spindle as Tool 1) and one reference frame (Reference 1).

5.Close the Settings window or select OK.
6.Select the ![]() Auto Setup button in Rhino.
Auto Setup button in Rhino.
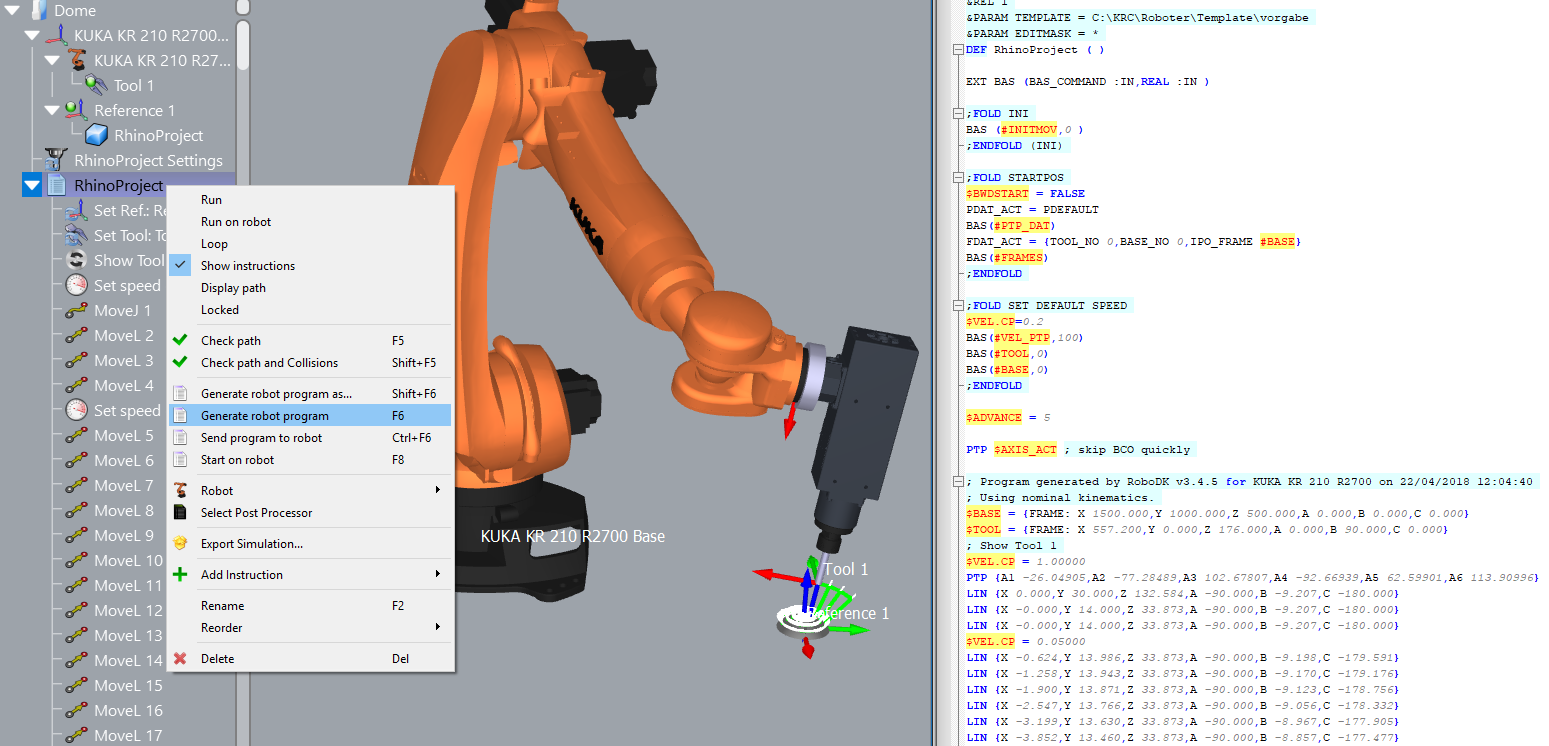
7.Select all the curves and surfaces and press Enter (or right mouse click). The project will be loaded in RoboDK as shown in the following image.
You should see the part loaded on the active reference frame (Reference 1) and a new Curve follow project in RoboDK that follows the curves with the active robot tool (Tool 1).
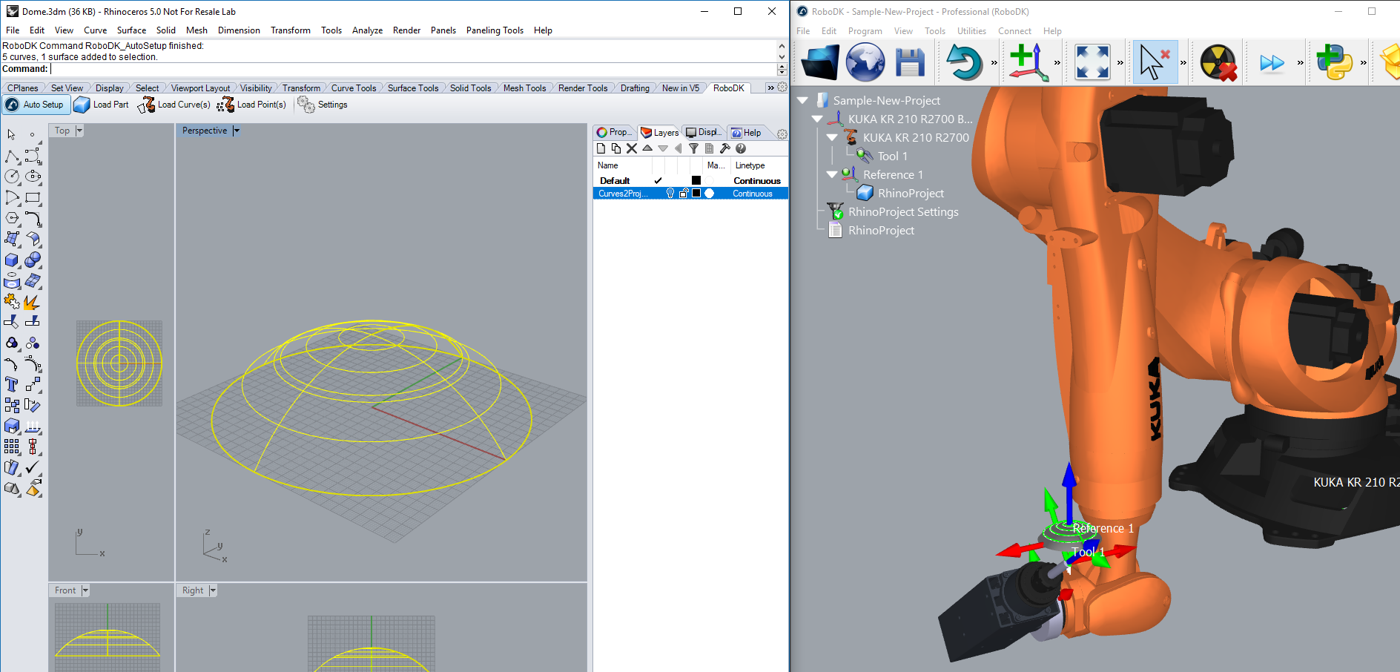
You can also see that the surface normals have been extracted in the opposite direction. Follow these steps to solve this issue:
8.Select ![]() Settings.
Settings.
9.Check the option Invert Normals.
10. Select OK.
11. Repeat steps 6 and 7.
You should now see the surface normals flipped and the approach movement comes from the top of the part. The robot should be able to move along the toolpath without any issues.
Double click the ![]() RhinoProject Settings from the RoboDK tree to open more options and customize the toolpath followed by the robot.
RhinoProject Settings from the RoboDK tree to open more options and customize the toolpath followed by the robot.
For example, you can select Show preferred tool path to see and modify the default orientation of the tool with respect to the part. Change the Path to tool offset value to define an additional rotation. To do so, you can enter a new value or just use the mouse wheel to see a quick preview of the result.
More information to change these settings is available in the robot machining section.
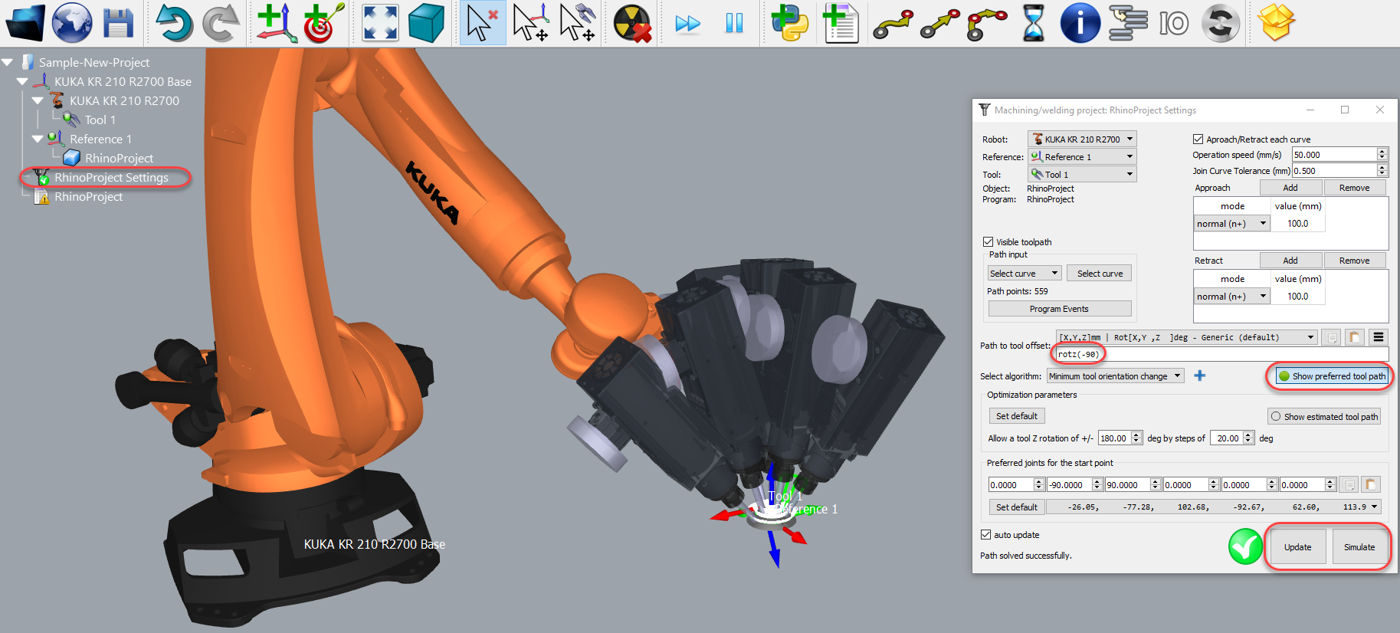
Finally, when the simulation produces the desired result you can generate the program or export the simulation:
12. Right click the program RhinoProject
13. Select Generate robot program (F6). The robot program will be generated and displayed.