It is possible to control the movement of a robot from the RoboDK API, for example, to program a robot from a Python program or a C# application.
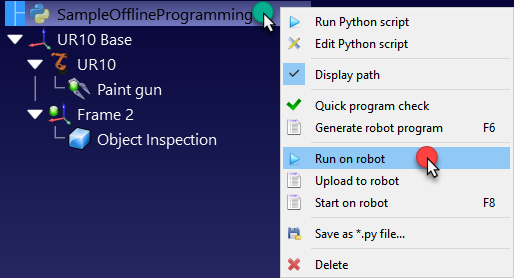
The Run on robot option is managed automatically when a Python program is run from RoboDK. Follow these steps to run a Python program on the robot:
1.Right click a ![]() Python program
Python program
2.Select ![]() Run on robot
Run on robot
The program should start running on the robot and the robot connection status will be updated accordingly.
If the program is executed outside the RoboDK’s GUI (for debugging purposes, or if we are using the RoboDK API for C# for example), we can set the RunMode using RDK.setRunMode to RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT. This will force the program to run on the robot. It is also possible to establish the connection using robot.Connect().
The following code shows a brief example to establish a connection with the robot directly from the API:
# Start the RoboDK API
RDK = Robolink()
robot = RDK.Item('',ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT)
# Connect to the robot using default connetion parameters
success = robot.Connect()
status, status_msg = robot.ConnectedState()
if status != ROBOTCOM_READY:
# Stop if the connection did not succeed
raise Exception("Failed to connect: " + status_msg)
# Set to run the robot commands on the robot
RDK.setRunMode(RUNMODE_RUN_ROBOT)
# Note: This is set automatically if we use
# robot.Connect() through the API
# Move the robot:
robot.MoveJ([10,20,30,40,50,60])
prog = RDK.Item('MainProgram', ITEM_TYPE_PROGRAM)
prog.setRunType(PROGRAM_RUN_ON_ROBOT) # Set the run on robot option
# Set to PROGRAM_RUN_ON_SIMULATOR to run on the simulator only
prog.RunProgram()
while prog.Busy() == 1:
pause(0.1)
print("Program done")